During the COVID-19 pandemic, many industries have had to find innovative solutions to provide their services in non-traditional ways, healthcare being no exception.
The healthcare industry has been increasing its focus on virtual patient interactions, and in a recent Telehealth Index survey, 66% of patients indicated that they were willing to use virtual care. Telemedicine apps, which facilitate these virtual interactions, have seen huge user growth during the COVID-19 outbreak, with some reporting app usage increases of up to 158% since the virus hit.
Telemedicine apps are playing a pivotal role in the evolution of medical care. Let’s explore some of the ways in which they’re impacting the healthcare industry.
1. Telemedicine minimizes human contact
During the pandemic, close contact should be avoided wherever possible; however, the average visit to the doctor could involve using public transport, sitting in a crowded waiting room, and physical contact with the doctor. Telemedicine apps have negated the need for patients to leave their homes, and in many cases, a patient can be diagnosed via video call; patients can even have their prescriptions filled and delivered to their door.
Live videoconferencing is one of the more common features of telemedicine apps, allowing users to contact a qualified healthcare professional over video chat in order to discuss diagnosis and treatment options. Remote patient monitoring (RPM) is another common feature of telemedicine, and involves a patient’s personal health or medical data being collected and sent to a hospital or clinic without even a video interaction.
Although many existing telemedicine apps are available, clinics and hospitals also have the option to create custom solutions, using resources such as this guide to developing a telemedicine app.
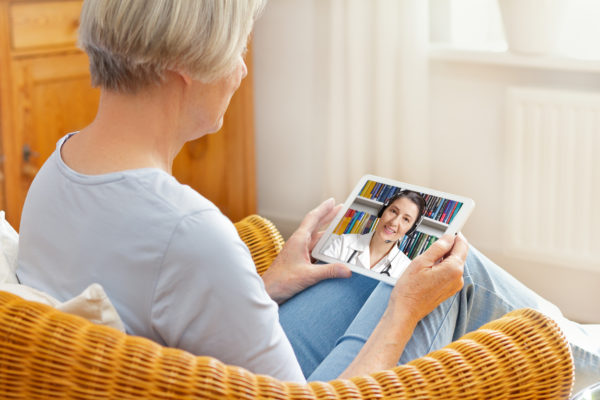

2. Telemedicine provides accessible solutions
Although barriers to telemedicine use must be constantly assessed, there is evidence that telemedicine is an effective way to provide healthcare to a wide variety of patients.
During a recent study, a medical clinic sought to discover if access to care was restricted during COVID-19. The study found that even though telemedicine was the only option for their patients between March and May 2020, patient visit numbers dropped by less than 25% from the same period in 2019, indicating that the majority of their clients were able to successfully use telemedicine technology.
Telemedicine apps are a convenient option for the 45% of US adults who report that their mental health has been negatively impacted by the pandemic. With around 35.7million people in the US living alone, telemedicine apps have been able to help battle the effects of isolation by connecting patients with qualified mental health experts from the comfort of their own homes.
3. Telemedicine sparks policy discussions
The interest in telemedicine apps is unlikely to fade any time soon; the global telehealth market is expected to hit $55.6 billion by 2025.
Given how rapidly telemedicine apps and services have become available, guidelines and policies outlining their obligations are somewhat lacking. While patient privacy is protected through HIPPA and the code of federal regulations, neither of these specifically address telehealth. This has led to many healthcare providers relying on app owners to implement appropriate privacy policies.
The rise of telemedicine options during COVID-19 has also caused a variety of healthcare industry regulations to be relaxed. This includes Medicare and Medicaid services extending reimbursement policies to cover telehealth options, given many restrictions on provider location have been impractical during stay-at-home orders.
4. Telemedicine improves work-life balance
Telemedicine apps play a critical role in improving the work-life balance of not only patients, but also their healthcare providers.
Patients who use telemedicine apps don’t need to take time out of their day to travel to an appointment, and sit in a waiting room if the doctors are running behind; patients can now continue to work or do things around their home while they wait for a doctor to contact them.
The number of US physicians expected to be using telehealth technology by 2022 is between 340,000 and 590,000; physicians who utilize telemedicine apps not only have the freedom to work from different locations (such as their homes); they may also find that they’re able to save money by moving to a smaller clinic, if they no longer need as large a space.
Conclusion
Telemedicine apps have played a huge role in allowing patients to seek medical care safely during the COVID-19 pandemic and are increasingly recognized as a valid healthcare option. If your business could benefit from using telehealth services, or you have a virtual health idea of your own, consider using telemedicine apps to bring your vision to life.
- How Telemedicine Apps Affect Healthcare in a Pandemic - April 9, 2021